Categories: Practical Electronics, How does it work
Number of views: 252103
Comments on the article: 21
How is an electronic transformer
 Externally electronic transformer It is a small metal, usually aluminum case, the halves of which are fastened with just two rivets. However, some companies produce similar devices in plastic cases.
Externally electronic transformer It is a small metal, usually aluminum case, the halves of which are fastened with just two rivets. However, some companies produce similar devices in plastic cases.
To see what is inside, these rivets can simply be drilled. The same operation will have to be done if an alteration or repair of the device itself is planned. Although at its low price it is much easier to go and buy something else than to repair the old. Nevertheless, there were many enthusiasts who not only managed to figure out the device design, but also developed several switching power supplies.
The circuit diagram for the device is not attached, as well as for all current electronic devices. But the circuit is quite simple, contains a small number of parts, and therefore the circuit diagram of an electronic transformer can be copied from a printed circuit board.
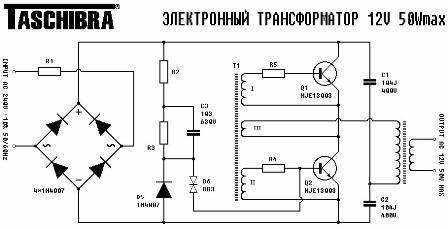
Figure 1 shows a similarly drawn Taschibra transformer circuit. Converters manufactured by Feron have a very similar circuit. The only difference is in the design of printed circuit boards and the types of parts used, mainly transformers: in Feron converters, the output transformer is made on a ring, while in Taschibra converters on a W-shaped core.
In both cases, the cores are made of ferrite. It should be noted right away that ring-shaped transformers with various modifications of the device are easier to rewind than W-shaped ones. Therefore, if an electronic transformer is purchased for experiments and alterations, it is better to buy a Feron device.
When using an electronic transformer for power only halogen lamps the name of the manufacturer does not matter. The only thing you should pay attention to is power: electronic transformers are available with a power of 60 - 250 watts.
Figure 1. Taschibra electronic transformer circuit
A brief description of the electronic transformer circuit, its advantages and disadvantages
As can be seen from the figure, the device is a push-pull oscillator made according to a half-bridge circuit. Two shoulder bridge made on transistors Q1 and Q2, and the other two arms contain capacitors C1 and C2, so this bridge is called a half-bridge.
Mains voltage rectified by a diode bridge is supplied to one of its diagonals, and the load is included in the other. In this case, this is the primary winding of the output transformer. According to a very similar scheme electronic ballasts for energy-saving lampsbut instead of a transformer, they include a choke, capacitors and filament of fluorescent lamps.
For management transistor operation windings I and II of the T1 feedback transformer are included in their base circuits. Winding III is current feedback, through which the primary winding of the output transformer is connected.
The control transformer T1 is wound on a ferrite ring with an external diameter of 8 mm. Basic windings I and II contain 3..4 turns each, and feedback winding III - only one turn. All three windings are made of wires in multi-colored plastic insulation, which is important when experimenting with the device.
On the elements R2, R3, C4, D5, D6, the startup circuit of the autogenerator is assembled at the time the entire device is connected to the network. Rectified input diode bridge mains voltage through resistor R2 charges capacitor C4. When the voltage on it exceeds the threshold of operation of the dynistor D6, the latter opens and a current pulse is generated on the basis of transistor Q2, which starts the converter.
Further work is carried out without the participation of the launch chain.It should be noted that the D6 dinistor is double-sided, can operate in AC circuits, in the case of direct current, the polarity of the inclusion does not matter. On the Internet, it is also called "diac."
The network rectifier is made on four diodes of the type 1N4007, the resistor R1 with a resistance of 1Ω and a power of 0, 125W is used as a fuse.
The converter circuit, as it is, is quite simple and does not contain any "excesses". After the rectifier bridge, not even a simple capacitor is provided for smoothing the ripples of the rectified mains voltage.
The output voltage directly from the output winding of the transformer is also supplied without any filters directly to the load. Are absent output voltage stabilization circuit and protection, therefore, during a short circuit in the load circuit several elements burn out at once, as a rule, these are transistors Q1, Q2, resistors R4, R5, R1. Well, maybe not all at once, but at least one transistor for sure.
And despite this seemingly imperfection, the circuit fully justifies itself when used in the normal mode, i.e. to power halogen lamps. The simplicity of the circuit determines its cheapness and widespread use of the device as a whole.
Study of the operation of electronic transformers
If a load is connected to an electronic transformer, for example, a 12V x 50W halogen lamp, and an oscilloscope is connected to this load, then on its screen you can see the picture shown in Figure 2.
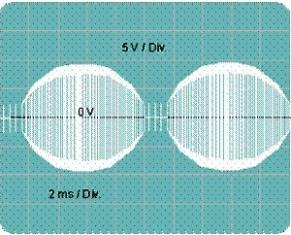
Figure 2. Oscillogram of the output voltage of the Taschibra 12Vx50W electronic transformer
The output voltage is a high-frequency oscillation with a frequency of 40 KHz, modulated at 100% frequency of 100 Hz, obtained after rectification of the mains voltage with a frequency of 50 Hz, which is quite suitable for supplying halogen lamps. Exactly the same picture will be obtained for converters of another power or another company, because the circuits practically do not differ from each other.
If connected to the output of the rectifier bridge electrolytic capacitor C4 47uFx400V, as shown by the dashed line in Figure 4, the load voltage will take the form shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3. Connecting a capacitor to the output of the rectifier bridge
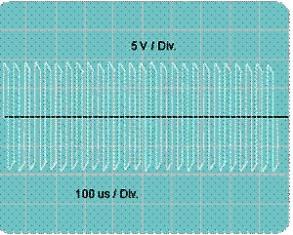
Figure 4. Voltage at the converter output after connecting the capacitor C5
However, we should not forget that the charging current of the additionally connected capacitor C4 will lead to the burnout, rather noisy, of the resistor R1, which is used as a fuse. Therefore, this resistor should be replaced with a more powerful resistor with nominal values of 22 Ohm2W, the purpose of which is simply to limit the charging current of capacitor C4. As a fuse, you should use a conventional 0.5A fuse.
It is easy to notice that the modulation with a frequency of 100 Hz has stopped, only high-frequency oscillations with a frequency of about 40 KHz remain. Even if there is no way to use an oscilloscope in this study, this indisputable fact can be noticed by a slight increase in the brightness of the bulb.
This suggests that the electronic transformer is quite suitable for creating simple switching power supplies. There are several options: using the converter without disassembling, only by adding external elements and with small changes to the circuit, very small, but giving the converter completely different properties. But we will talk about this in more detail in the next article.
Boris Aladyshkin
Continuation of this topic: How to make a power supply from an electronic transformer
See also at e.imadeself.com
: