Categories: Novice electricians, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 62781
Comments on the article: 6
Which protection devices are better: fuses or circuit breakers?
 When operating a domestic and industrial electrical network, there are always risks of electric injuries or equipment damage. They can occur at any time when critical conditions appear. To reduce such consequences allow protective devices. Their use significantly increases the safety of using electricity.
When operating a domestic and industrial electrical network, there are always risks of electric injuries or equipment damage. They can occur at any time when critical conditions appear. To reduce such consequences allow protective devices. Their use significantly increases the safety of using electricity.
Electric circuit protection work based on:
-
fuse;
-
mechanical circuit breaker.
Principle of operation and fuse arrangement
Two ingenious scientists, Joule and Lenz, simultaneously established the laws of mutual relations between the magnitude of the passing current in the conductor and the release of heat from it, revealing the dependences on the circuit resistance and the length of time.
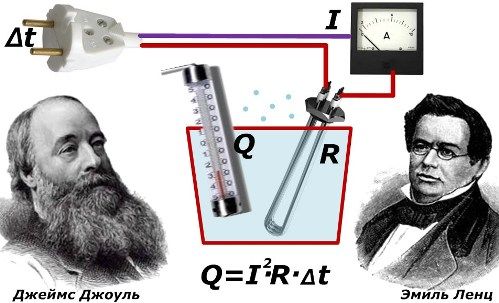
Joule Lenz Law
Their findings made it possible to create the simplest protective structures based on the thermal effect of current on the metal of the wire. At electrical fuses a thin metal insert is used through which the total current of the circuit is passed.
With the nominal parameters of electric power transmission, this “wire” reliably withstands the heat load, and with excess of its values above the norm, it burns out, breaking the circuit and removing voltage from consumers. To restore the operation of the circuit, it is necessary to replace the burned out element: a fuse.
It is clearly visible on fuse structures for household TV and radio equipment with glass, transparent insert housings.
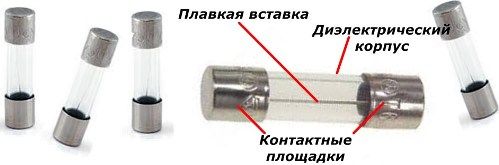
Fuses for household radio equipment
At its ends, special metal pads are mounted that create electrical contact when installed in sockets. This principle is embodied in electrical plugs with fusible inserts, which for many decades have protected our parents and older generations from damage in electrical wiring.
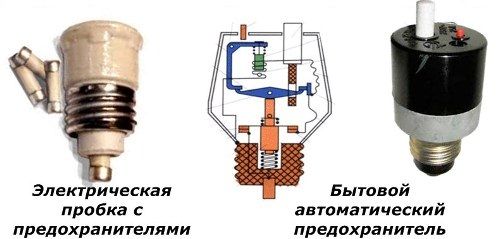
Ordinary and automatic fuses for old wiring
In the same form, automatic designs were developed that screwed into nests instead of plugs. But when triggered, they did not need to replace the components. To restore power supply, just drown the button inside the case.
In these ways, the old electrical inputs to the apartment were protected. Then along with fuses began to appear circuit breakers.

Apartment entry protection
Fuse selection is based on:
-
rated currents of the fuse itself and its insertion;
-
minimum / maximum multiples of the test current;
-
maximum disconnected electric current and the possibility of rupture of the transported power;
-
protective characteristics of the fuse;
-
fuse rated voltage;
-
compliance with the principles of selectivity.
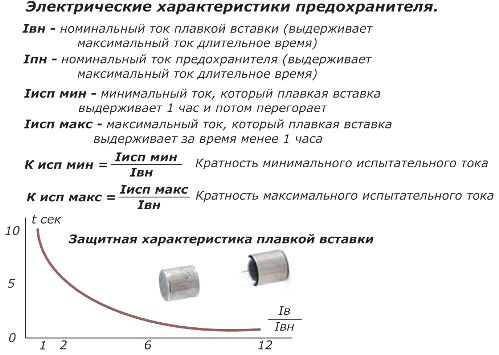
Electrical characteristics of the fuse
Fuses have a simple design. They are widely used in electrical installations, including high-voltage equipment up to 10 kV, for example, in the protection of measuring voltage transformers.

Industrial High Voltage Fuses
The principle of operation and the device circuit breaker
The purpose of a mechanical switching device, called a circuit breaker, is:
-
turning on, passing, disconnecting currents in normal circuit mode;
-
automatic voltage relief from electrical installations during emergency conditions, for example, currents of metal short circuits. Circuit breakers operate in reusable short-circuit and overload protection modes.The possibility of repeated use is considered their main difference from the fuse.
In the days of the USSR, in the energy sector, circuit breakers of the AP-50, AK-50, AK-63, AO-15 series were widely used.
AP-50 Series Switches

Circuit breakers in relay protection and automation panels
Read also: How relay protection and automation (RPA) work
In modern electrical circuits, advanced designs of foreign and domestic manufacturers work.

Modern circuit breakers
All of them are enclosed in dielectric housings, have common executive bodies, providing:
1. thermal trip of the circuit with a slight excess of the permissible current value;
2. electromagnetic cut-off during sudden load surges;
3. arc suppression chambers;
4. contact systems.
In the case of heating with the energy of the generated heat, a bimetallic plate works, bending from the temperature effect until the trip mechanism is activated. This function depends on the amount of heat released and stretched in time to a certain point.
The cut-off acts as quickly as possible from the operation of the electromagnetic solenoid with the appearance of an electric arc. To extinguish it, special measures are applied.
Reinforced contacts designed for multiple breaks short circuit currents in the circuit.
Operational differences of circuit breakers from fuses
The protective properties of both methods are time-tested, and each method requires analysis of specific operating conditions when assessing the cost of the structure, taking into account the duration and reliability of the work.
Circuit breakers simpler arranged, disconnect the circuit one-time, cheaper. They can relieve stress manually, but this is usually not very convenient. Moreover, with slight exceeding currents, they disconnect the load for a long time. This factor may cause increased fire hazard.
Any fuse protects only one phase of the network.
Circuit breakers harder, more expensive, more functional. But they are more precisely tuned to the settings of the protected circuitry, are selected according to the working rated current, taking into account the switched capacities.
Cases of modern thermoset automats are highly resistant to thermal effects. They do not melt, are resistant to ignition. For comparison: the polystyrene case of the old circuit breakers could withstand temperatures no higher than 70 degrees.
The design allows you to select models for the simultaneous opening of one to four electrical circuits. If fuses are used in a three-phase circuit, they will relieve voltage from the circuit with different time delays, which may become an additional cause of the accident.
Fuses operate on current, regardless of its characteristics. Circuit breakers are selected under load and classified by letters:
-
A - electric networks of extended length;
-
B - lighting of corridors and platforms;
-
C - power and lighting systems with moderate starting currents;
-
D - the prevailing load from the inclusion of electric motors with large starting parameters;
-
K - inductive furnaces and electric dryers;
-
Z is electronics.
See also: Characteristics of circuit breakers
The advantages of switches are obvious:
-
reliability;
-
quick shutdown time of accidents;
-
variety of designs;
-
more protective functions;
-
ability to switch multiple sections;
-
fire hazard reduction;
-
simplicity of manual commutation;
-
convenient installation.
That is why automatic devices are popular.
However, science is constantly evolving and introducing new technical solutions. For example, Murller began to mass-produce modern fuses, switches, disconnectors with a wide range of capabilities.

Modern Murller fuse switch disconnectors
Even their name speaks of the variety of functions of new devices.
Therefore, choosing protection for the electrical circuit, analyze the design of the model you like and its capabilities, taking into account the individual characteristics of your electrical consumers at minimal cost.
See also at e.imadeself.com
:
