Categories: Novice electricians, Automata and RCD
Number of views: 446961
Comments on the article: 35
Characteristics of circuit breakers
 A circuit breaker, or, more simply, an automaton, is an electrical device familiar to almost everyone. Everyone knows that the machine disconnects the network when there are any problems in it. If not smart, then these problems are too much electric current. Excessive electric current is dangerous for all conductors and household electrical equipment to fail, possibly overheating, igniting, and, accordingly, a fire. Therefore, protection against high currents is a classic of electrical circuits, and it existed even at the dawn of electrification.
A circuit breaker, or, more simply, an automaton, is an electrical device familiar to almost everyone. Everyone knows that the machine disconnects the network when there are any problems in it. If not smart, then these problems are too much electric current. Excessive electric current is dangerous for all conductors and household electrical equipment to fail, possibly overheating, igniting, and, accordingly, a fire. Therefore, protection against high currents is a classic of electrical circuits, and it existed even at the dawn of electrification.

Any overcurrent protection device has two important tasks:
1) in time and accurately recognize too high current;
2) break the circuit before this current can cause any damage.
At the same time, high currents can be divided into two categories:
1) high currents caused by network congestion (for example, the inclusion of a large number of household electrical appliances, or a malfunction of some of them);
2) short circuit overcurrentswhen the neutral and phase conductors directly close together, bypassing the load.
It may seem strange to someone, but it is with the overcurrents of the short circuit that everything is extremely simple. Modern electromagnetic releases easily and completely accurately determine the short circuit and disconnect the load in fractions of a second, avoiding even the slightest damage to the conductors and equipment.
Overload currents are becoming more complicated. Such a current is not much different from the rated current, for some time it can flow along the circuit without any consequences. Therefore, there is no need to turn off such a current instantly, especially since it could have arisen very briefly. The situation is aggravated by the fact that each network has its own maximum overload current. And not even one.
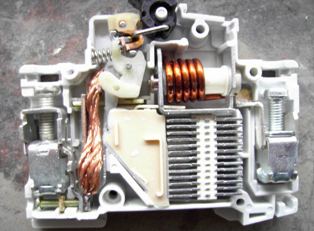
Circuit breaker device
There are a number of currents, for each of which it is theoretically possible to determine your maximum network shutdown time, from a few seconds to tens of minutes. But false positives must also be eliminated: if the current for the network is harmless, then the shutdown should not occur in a minute or an hour - never at all.
Turns out that the setting of the operation of the overload protection must be adjusted to a specific load, change its ranges. And, of course, before installing the overload protection device, it must be loaded and checked.
So, in modern “automatic machines” there are three types of releases: mechanical - for manual on and off, electromagnetic (solenoid) - for disconnecting short-circuit currents, and the most difficult - thermal for overload protection. It is the characteristic of thermal and electromagnetic releases that is circuit breaker characteristic, which is indicated by a Latin letter on the case in front of a number indicating the current rating of the device.
This characteristic means:
a) the operating range of the overload protection, due to the parameters of the built-in bimetallic plate, bending and breaking the circuit when a large electric current flows through it. Fine tuning is achieved by an adjusting screw that tightens this same plate;
b) the response range of the overcurrent protection, due to the parameters of the built-in solenoid.
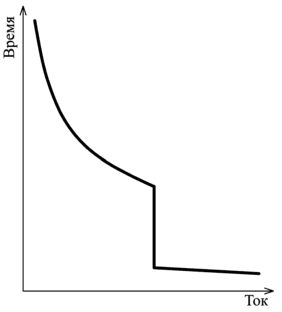
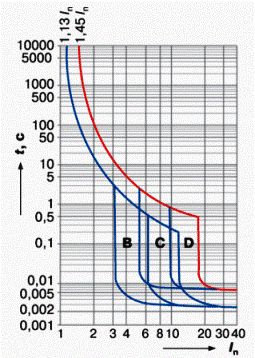
Time-current characteristic of a circuit breaker
We list below characteristics of modular circuit breakers, talk about how they differ from each other and what are the machines that have them for. All characteristics are the relationships between the load current and the trip time at that current.
1) Characteristic MA - absence of thermal release. In fact, it really is not always needed.For example, the protection of electric motors is often carried out with the help of overcurrent relays, and an automaton in this case is needed only to protect against short circuit currents.
2) Characteristic A. The thermal release of an automaton of this characteristic can trip even at a current of 1.3 of the nominal. In this case, the shutdown time will be about an hour. At a current exceeding the nominal twice, the electromagnetic trip can come into effect, which works in about 0.05 seconds. But if the solenoid still does not work when the current is doubled, then the thermal release remains “in the game”, disconnecting the load after about 20-30 seconds. At a current exceeding the rated three times, the electromagnetic release is guaranteed to operate in hundredths of a second.
Circuit Breakers Characteristic A are installed in those circuits where short-term overloads cannot occur in normal operating mode. An example is circuits containing devices with semiconductor elements that can fail with a small excess of current.
3) Characteristic B. The characteristic of these machines differs from the characteristic A in that the electromagnetic release can only operate at a current exceeding the rated one not by two, but by three or more times. The response time of the solenoid is only 0.015 seconds. The thermal release, when the machine B is triple overloaded, will trip after 4-5 seconds. Guaranteed operation of the machine occurs at five times overload for alternating current and at a load exceeding the nominal 7.5 times in DC circuits.
Circuit Breakers Characteristics B they are used in lighting networks, as well as other networks in which the starting increase in current is either small or absent.
4) Characteristic C. This is the most famous feature for most electricians. Automatic machines C are distinguished by even greater overload capacity compared with automatic machines B and A. Thus, the minimum operating current of the electromagnetic release of an automatic device of characteristic C is five times the rated current. At the same current, the thermal release trips after 1.5 seconds, and the guaranteed operation of the electromagnetic release occurs with a ten-fold overload for alternating current and a 15-fold overload for direct current circuits.
Circuit Breakers C They are recommended for installation in networks with a mixed load, which assumes moderate inrush currents, due to which household electrical panels contain precisely this type of machine.
Characteristics of circuit breakers B, C and D
5) Characteristic D - It has a very large overload capacity. The minimum response current of the electromagnetic solenoid of this machine is ten rated currents, and the thermal release can trip in 0.4 seconds. Guaranteed operation is ensured with a twenty-fold overcurrent.
D circuit breakers designed primarily for connecting motors with large inrush currents.
6) Characteristic K It differs by a large spread between the maximum operating current of the solenoid in AC and DC circuits. The minimum overload current at which the electromagnetic release can trip is eight rated currents for these machines, and the guaranteed operation current of the same protection is 12 rated currents in the AC circuit and 18 rated currents in the DC circuit. The response time of the electromagnetic release is up to 0.02 seconds. The thermal release of the automatic machine K can operate at a current exceeding the nominal one-fold by only 1.05 times.
Due to such features of the K characteristic, these machines are used to connect a purely inductive load.
7) Characteristic Z also has differences in the currents of guaranteed operation of the electromagnetic release in the AC and DC circuits.The minimum possible operating current of the solenoid for these machines is two rated, and the guaranteed operating current of the electromagnetic release is three rated currents for AC circuits and 4.5 rated currents for DC circuits. The thermal release of automatic machines Z, like that of automatic machines K, can operate at a current of 1.05 of the nominal.
Z machines are used only for connecting electronic devices.
Alexander Molokov
See also at e.imadeself.com
: