Categories: Practical Electronics, Electrician Secrets
Number of views: 67331
Comments on the article: 0
How to determine the malfunction of thyristors
 Loss of thyristor performance may occur due toand:
Loss of thyristor performance may occur due toand:
a) open circuit inside the device (combustion);
b) loss of controllability (combustion of the control electrode circuit);
c) loss of locking ability in the forward or reverse direction (breakdown);
d) breakage of conclusions.
An inoperative thyristor can be detected using an AC voltmeter, an ohmmeter, or a test circuit.
An inoperative thyristor in a circuit under AC voltage can generally be detected with a voltmeter.
The variety of circuits and variable values of the thyristor control angles do not allow specifying specific values of the voltage on the thyristor for various reasons for inoperability.
Tentatively, during combustion, the voltage on the thyristor will be higher, and during breakdown less than that of a similar operable device.
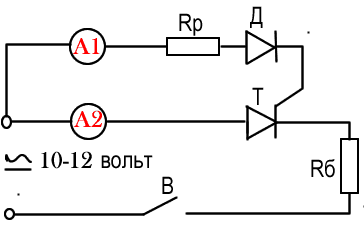
The combustion of the thyristor or its control transition can be determined using a test circuit:

The most common values of control currents are approximately an order of magnitude lower than the maximum values.
The resistor resistance is selected from the condition that the thyristor direct current is limited to 30-50 mA for low power devices and 400 to 500 mA for medium and high power.
The moment and currents of inclusion and control are controlled by ammeters.
See also at e.imadeself.com
: