Categories: How does it work
Number of views: 16738
Comments on the article: 1
How are non-contact thermometers arranged and working?
Non-contact thermometers or pyrometers are today convenient devices for remote temperature measurement of various objects, liquids or solids. They are widely used in the power industry for the operational control of the temperature of important areas, in the electric power industry to ensure fire safety, in laboratory conditions, in enterprises, in construction for calculating heat losses, in everyday life, in security systems, and much more.
The first such device was invented back in 1731 by the Dutch physicist Peter van Mushenbruck, and measurements were made visually, it was possible to judge the temperature by the color of a red-hot body. But modern types of pyrometers have greatly expanded their field of application, and even temperature close to zero can be measured degrees Celcius and below. However, the principle has remained generally the same - the power of the thermal radiation emanating from the object is measured, and a conclusion about its temperature is drawn from this. Measurements are carried out in the infrared and visible spectral range.
In 1967, the American company Wahl introduced the first portable pyrometer, since it was in the 60s that the most important scientific discoveries were made, which laid the foundation for the development of the development of industrial pyrometers with sufficiently high characteristics with small dimensions. The principle based on the construction of comparative parallels, using an infrared receiver capable of determining the amount of thermal energy emitted by the object, has significantly expanded the range of temperature measurements for both liquid and solid bodies.

At the moment, pyrometers are very popular, and are widely used for non-contact measurement at a distance of the temperature of objects in everyday life, in the housing and utilities sector, in enterprises, wherever temperature control of various processes is required at the production stages and during the operation of many devices. Pyrometers make it possible to safely measure the temperature of even a hot body, without the need to physically contact it.
Pyrometers are optical, radiation and color. The first ones allow a visual comparison of the color of the heated body with the color of the reference thread, and thus determine its temperature. Radiation recalculates the power of thermal radiation, and can measure a fairly wide range of temperatures. Color compares the thermal radiation of the object in various spectra, and then calculate its temperature, such pyrometers also have a wide range of measurements.

All pyrometers can also be divided into low temperature and high temperature. Low-temperature even allow you to measure temperatures below zero, and high-temperature have a high upper limit of measurement.

According to the type of execution, the pyrometers differ in portable and stationary. The latter are used in large industrial enterprises for very precise and continuous control of the technological process, for example, in the production of molten plastics and metals. Portable pyrometers are popular in everyday life and as portable thermometers in various industries, they clearly present information about the temperature on the display in text or graphic form.
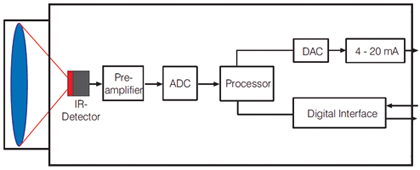
The device and operation of a modern infrared pyrometer can be described as follows. The heat ray received by the device is focused by the optical system, and then falls on temperature sensor (this is the primary pyrometric transducer), an electric signal is obtained at the output of the pyrometric transducer, the value of which is proportional to the temperature value of the object under study. The signal received from the sensor then passes through the electronic transducer (this is a secondary pyrometric transducer), and enters the measuring and calculating device and is processed in it. The calculation result is displayed on the display, in the most popular models - in the form of numbers.

So, in order to get the exact value of the surface temperature of the studied object, the user only needs to turn on the device, point it at the studied object and press the start button. The measurement result will be displayed on the display in the form of numbers or graphically in the form of a multi-colored image, where spectrally the areas of low, medium and high temperatures will be highlighted in different colors.
Main technical characteristics of pyrometers:
-
optical resolution (models with a resolution of 2: 1 to 600: 1 are available);
-
measured temperature range (maximum - from -50 ° C to + 4000 ° C);
-
measurement resolution - typical values are 0.1 ° C or 1 ° C;
-
measurement accuracy (± 1.5% is considered optimal);
-
speed (modern pyrometers require no more than 1 second);
-
emissivity - can be custom or fixed;
-
targeting method - laser designator or optical guidance.

The most important parameters of the pyrometers are setting the degree of blackness of the object and the optical resolution (indicator of sight) of the device. The optical resolution of the pyrometer is characterized by the ratio of the distance from the pyrometer to the surface of the body to the diameter of a round spot on the surface of the body (the area of accurate temperature measurement is limited by this spot), the temperature of which is measured.
So, if temperature measurements are required from a short distance, a pyrometer with a small resolution, for example, 4: 1, is used, and if measurements are planned from several meters, the resolution should be larger so that foreign objects do not fall into the field of view of the device. Often, pyrometers are equipped with a laser target designator to more accurately point the instrument at the object under study.
The degree of blackness or emissivity of the material characterizes the reflectivity of the material itself, the temperature of which is remotely measured by a pyrometer. For an infrared thermometer, which are the pyrometers popular today, this indicator is extremely important. It determines the ratio of the energy emitted by the investigated surface to the energy emitted by a completely black body at the same temperature, and the value of this parameter lies in the range from 0 to 1. Thus, oxidized steel has a blackness of 0.85, and polished - 0.075.
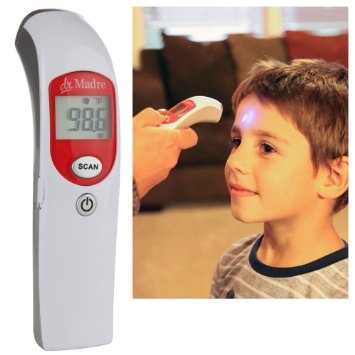
On many online trading sites, and in electronics stores, portable laser-oriented pyrometers are widely represented today, which are perfect for household needs, as well as special medical pyrometers to replace mercury thermometers. For industrial purposes, more accurate and more expensive pyrometers are used, which have, among other things, auxiliary means of transmitting information and the ability to connect to a computer and special devices.
See also: Temperature sensors - thermistors
See also at e.imadeself.com
:
