Categories: Novice electricians, Electrician Secrets, Safety precautions
Number of views: 136430
Comments on the article: 15
What is protective grounding and how does it work

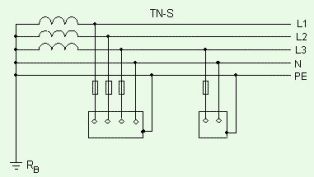
Zeroing is a system of measures that ensure safety in case of single-phase short circuits to the case in electrical installations with a dead-grounded neutral voltage of up to 1000 V. Zeroing provides protection by automatically disconnecting the damaged section of the electrical installation from the network and reducing the voltage on the bodies of the bullet-proof electrical equipment until it is safe for the duration of protection operation.
Thus, grounding combines the functions of two types of protective devices - grounding and protective shutdown and includes the following elements:
-
grounding line - a metal conductor connected to the neutral of the transformer, to which metal elements of electrical equipment are connected, normally isolated from voltage;
-
branch line to electrical equipment - a metal conductor that connects the elements of electrical equipment to be neutral, with the main line;
-
disconnecting device - a switching device through which electrical equipment is connected to the supply network, responding to a single-phase circuit current to the housing and disconnecting emergency electrical equipment from the network;
-
repeated grounding of the trunk - communications of the trunk with the ground through grounding conductors with low resistance, performed on certain sections of the grounding system.
Protective grounding, purpose and principle of action
Currently, there are several different power supply systems for consumers with voltages up to 1000 V, however, in Russia, the main one in this case is a system with dead-grounded neutral. It is such a system that is used in each of our homes.
With the apparent complexity of the name, everything is extremely simple. In such a system, the neutral point of the transformer at the substation is directly connected to the ground. The main measure of protection against accidental undervoltage in this case is protective grounding, that is, a special connection of any metal part of the household appliance with the neutral of the transformer.
Since, as noted above, in such systems the neutral is deafly connected to the ground, in essence protective grounding is nothing but one of the types of grounding.
 In each of our home outlets, when wiring is correctly performed in the house, there is a grounding contact. It is through it, when the appliance is turned on, we connect its body to the neutral point of the transformer.
In each of our home outlets, when wiring is correctly performed in the house, there is a grounding contact. It is through it, when the appliance is turned on, we connect its body to the neutral point of the transformer.
The essence of protective grounding is as follows. Regulatory documents regulate the permissible time for disconnecting a damaged line with a short circuit of no more than 0.4 seconds. It is during this time that it is believed that a person has every chance of staying alive when exposed to stress.
When performing protective grounding, the resistance of the phase-zero loop is significantly reduced and is ensured sufficient short circuit current for operation of the protection device (fuse or circuit breaker) for a time not exceeding 0.4 seconds.
 In the absence of protective grounding, or as it is called “grounding” in everyday life, the short circuit current due to high resistance may be insufficient for the protection to operate and a damaged household appliance may end up under voltage dangerous to humans for a long time.
In the absence of protective grounding, or as it is called “grounding” in everyday life, the short circuit current due to high resistance may be insufficient for the protection to operate and a damaged household appliance may end up under voltage dangerous to humans for a long time.
Protective grounding is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the current Rules of Electrical Installations (PUE). As a rule, a third core of the wire is used for this, or a separately laid copper conductor with a cross section of at least 4 mm.sq.
In addition, in networks with dead-grounded neutral, it is strictly forbidden to ground household appliances to a separate ground loop that is not connected to the neutral point of the transformer. For example, simply by connecting a ground contact sockets with a metal rod driven by itself under the window.
Protective grounding
The same applies to attempts to "ground" on the heating or water supply system of the apartment. In this case, the short-circuit current can be quite low due to the fact that the earth and the additional ground loop (usually home-made production) have much greater resistance than a special zero protective conductor.
In general, protective grounding plays a huge role in ensuring the electrical safety of your home, and you should pay maximum attention to the quality and correctness of its implementation.
See also at e.imadeself.com
: