Categories: Sharing experience, Electric motors and their application
Number of views: 559167
Comments on the article: 27
How to determine the working and starting windings of a single-phase motor

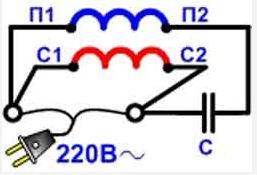
Single-phase motors are electric machines of low power. In the magnetic circuit of single-phase motors there is a two-phase winding, consisting of the main and starting windings.
Two windings are needed in order to cause the rotation of the rotor of a single-phase motor. The most common motors of this type can be divided into two groups: single-phase motors with a starting winding and motors with a working capacitor.
For engines of the first type, the starting winding is switched on through the capacitor only at the time of starting and after the engine has developed a normal rotation speed, it is disconnected from the network. The engine continues to work with one working winding. The value of the capacitor is usually indicated on the nameplate of the motor and depends on its design.
For single-phase asynchronous AC motors with a working capacitor, the auxiliary winding is switched on continuously through the capacitor. The value of the capacitor’s working capacity is determined by the design of the engine.
That is, if the auxiliary winding of a single-phase motor is starting, its connection will only occur during start-up, and if the auxiliary winding is capacitor, then its connection will occur through a capacitor that remains on during the operation of the motor.
It is necessary to know the device of the starting and working windings of a single-phase motor. The starting and working windings of single-phase motors differ both in the cross-section of the wire and in the number of turns. The working winding of a single-phase motor always has a larger wire cross section, and therefore its resistance will be less.
Look at the photo clearly shows that the cross-section of the wires is different. A winding with a smaller cross section is the starting one. You can measure the resistance of the windings with both arrow and digital testers, as well as an ohmmeter. A winding in which the resistance is less is a working one.
Fig. 1. The working and starting windings of a single-phase motor
And now a few examples you may come across:
If the motor has 4 outputs, then finding the ends of the windings and after measuring, you will now easily understand these four wires, the resistance is less - working, the resistance is more - starting. Everything is connected simply, 220v is supplied to thick wires. And one tip of the starting winding, on one of the workers. Which of them does not differ, the direction of rotation does not depend on this. The same is how you insert the plug into the outlet. The rotation will change, from connecting the starting winding, namely - changing the ends of the starting winding.
The following example. This is when the engine has 3 pins. Here the measurements will look as follows, for example - 10 ohms, 25 ohms, 15 ohms. After several measurements, find the tip from which the readings, with the other two, will be 15 ohms and 10 ohms. This will be one of the network wires. The tip, which shows 10 ohms, is also network and the third 15 ohms will be the trigger, which is connected to the second network through a capacitor. In this example, the direction of rotation, you will not change what it will be. Here, in order to change the rotation, it will be necessary to get to the winding circuit.
Another example where measurements can show 10 ohms, 10 ohms, 20 ohms. This is also one of the varieties of windings. Such, went on some models of washing machines, and not only. In these engines, the working and starting ones are the same windings (according to the design of three-phase windings). There is no difference what kind of worker you will have and what kind of starting winding. Connecting the starting winding of a single-phase motoralso carried through a capacitor.
See also at e.imadeself.com
: