Categories: Featured Articles » Electrician at home
Number of views: 155557
Comments on the article: 3
Power supply of an apartment building
 In order to correctly understand the various power supply schemes for residential buildings, you need to know about three categories of ensuring the reliability of power supply of electrical installations. The simplest category is the third. It provides for the power supply of a residential building from a transformer substation via a single electric cable. In this case, in the event of an emergency, the break in the power supply of the house should be less than 1 day.
In order to correctly understand the various power supply schemes for residential buildings, you need to know about three categories of ensuring the reliability of power supply of electrical installations. The simplest category is the third. It provides for the power supply of a residential building from a transformer substation via a single electric cable. In this case, in the event of an emergency, the break in the power supply of the house should be less than 1 day.
In the second category of reliability of power supply, the residential building is powered by two cables connected to different transformers. In this case, when a single cable or transformer fails, the power supply of the house for the duration of the troubleshooting is carried out through one cable. A break in the power supply is allowed for the time required by the on-duty electrical personnel to connect the loads of the whole house to a working cable.
There are two varieties of power supply at home from two different transformers. Either the load of the house is evenly distributed across both transformers, and in emergency mode connected to one, or in the operating mode one cable is involved, and the second is a backup. But in any case, the cables are connected to different transformers. If in switchboard house two cables are laid, one of which is redundant, but it is possible to connect these cables to only one transformer of the substation, then we have only the third category of reliability.
In the first category of reliability of power supply, the residential building is powered by two cables, as well as in the second category. But if the cable or the transformer fails, the loads of the whole house are connected to the working cable using the automatic transfer switch (ATS).
There is a special group of power consumers (fire alarm, smoke exhaust systems in case of fire, emergency lighting and some others), which should always be powered by the first category of reliability. To do this, use backup power sources - batteries and small local power plants.
According to existing standards for the third category of reliability, electricity is supplied to houses with gas stoves with a height of not more than 5 floors, houses with electric stoves with the number of apartments in the house less than 9 and houses of gardening associations.
Electricity supply in the second category of reliability is subject to houses with gas stoves with a height of more than 5 floors and houses with electric stoves with the number of apartments more than 8.
In the first category of reliability, electricity is supplied to the heating units of apartment buildings, in some houses and elevators. It should be noted that in the first category they mainly supply electricity to some public buildings: these are buildings with more than 2,000 employees, operating and maternity wards of hospitals, etc.
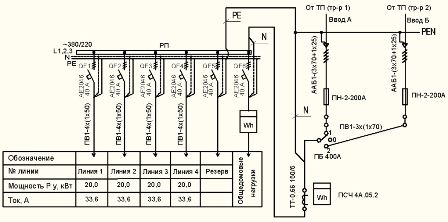
The figure shows power supply scheme of the four access house, powered by the second category of reliability with a backup cable. Switching the power cables is carried out by a reversing switch having the positions "1", "0" and "2". In position “0” both cables are disconnected. From circuit breakers QF1 ... .QF4 the lines that go along the vertical risers, from which the power is taken to the apartments, are powered. General house loads: lighting of stairs, basements, lamps above the entrance doors to the entrances feed a separate group containing their own electricity metering.
Fig. 1. Electricity scheme of an apartment building
Depending on the number of apartments in the house, all electrical equipment can be placed in one electrical cabinet or in several.How the electrical equipment of switchboard houses looks like is shown in the photographs. In the photo 1 - input devices and metering units. In the photo 2 - reversible switch with fuses. In the photo 3 - circuit breakers on the outgoing lines.

Introductory devices and metering units of an apartment building

Reversible circuit breaker with fuses
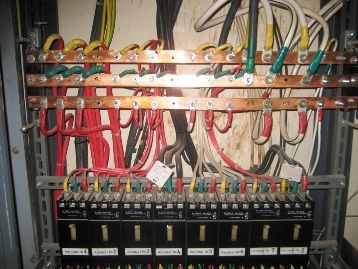
Outgoing circuit breakers
If the school had the subject: “Fundamentals of the power supply of our home,” then accidents caused by the failure of various power switches and disconnectors on power lines and in transformer substations would happen much less frequently. We are taught from childhood to wash our hands before eating and tell how to cross the road. But no one teaches us that if the light goes out in the apartment, then you should immediately disconnect from the network all powerful electrical appliances: irons, heaters and electric stoves.
For example, if the network was disconnected as a result of a fuse blowing out in an electrical panel house, then to restore power supply, electricians will need to turn off the switch, replace the fuse, and turn on the switch again. The lifespan of all switching devices depends very much on the magnitude of the switched load.
If all the residents of the house disconnected their electrical appliances from the mains during a power failure, then such switching on would occur at much lower currents and the circuit breakers would last much longer.
In our example, when electricians turn off the circuit breaker, a bright flash can be observed in the circuit of two phases with unburnt fuses at the moment of disconnection of the contacts - an arc will flash for a split second, from which the contacts gradually burn out.
See also at e.imadeself.com
: